
Role of CX3CL1/Fractalkine in Osteoclast Differrentiation and Bone Resorption
Koizumi K1, Saitoh Y, Minami T, Takeno N, Tsuneyama K, Miyahara T, Nakayama T, Sakurai H, Takano Y, Nishimura M, Imai T, Yoshie O, Saiki I.
1Division of Pathogenic Biochemistry, Institute of Natural Medicine, University of Toyama, Toyama, Japan. kkoizumi@inm.u-toyama.ac.jp
J Immunol. 2009 Dec 15;183(12):7825-31
Abstract
The recruitment of osteoclast precursors toward osteoblasts and subsequent cell-cell interactions are critical for osteoclast differentiation. Chemokines are known to regulate cell migration and adhesion. CX3CL1 (also called fractalkine) is a unique membrane-bound chemokine that has dual functions for cells expressing its receptor CX3CR1: a potent chemotactic factor in its soluble form and a type of efficient cell adhesion molecule in its membrane-bound form. In this paper, we demonstrate a novel role of CX3CL1 in osteoblast-induced osteoclast differentiation. We found that osteoclast precursors selectively expressed CX3CR1, whereas CX3CL1 is expressed by osteoblasts. We confirmed that soluble CX3CL1 induced migration of bone marrow cells containing osteoclast precursors, whereas immobilized CX3CL1 mediated firm adhesion of osteoclast precursors. Furthermore, a blocking mAb against CX3CL1 efficiently inhibited osteoclast differentiation in mouse bone marrow cells cocultured with osteoblasts. Anti-CX3CL1 also significantly suppressed bone resorption in neonatal mice by reducing the number of bone-resorbing mature osteoclasts. Collectively, CX3CL1 expressed by osteoblasts plays an important role in osteoclast differentiation, possibly through its dual functions as a chemotactic factor and adhesion molecule for osteoclast precursors expressing CX3CR1. The CX3CL1-CX3CR1 axis may be a novel target for the therapeutic intervention of bone resorbing diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoporosis, and cancer bone metastasis.
<Keyword>
CXCL1/ fractalkine : 膜結合型のケモカイン。ADAM10やADAM17により細胞膜からcleavingされ、分泌型フラクタルカインはNK細胞、T細胞、単球に対する細胞遊走活性を示す。
CX3CR1 : フラクタルカイン受容体。単球、リンパ球、樹状細胞で発現しており、他関節滑膜線維芽細胞でも発現が確認されている。
CX3CL1とRAについて: 関節リウマチ滑液中に分泌型CX3CL1は高発現しており、炎症細胞の活性化内皮細胞への接着や関節への浸潤、あるいはサイトカインの産生に関与している。滑膜の増生にも関与している可能性がある。
<Methods and Results>
1.RANL-induced differentiation of osteoclasts in vitro
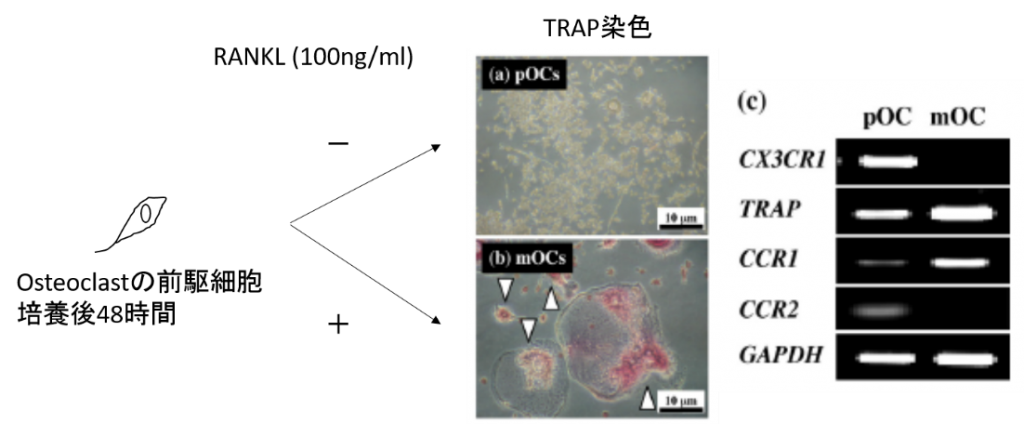
同様の結果をmouseのsplenocytesとpOCのcell line(RAW264.7)を使用して確認した。
2.CX3CL1 directly mediates the migration and adhision but not differentiation of pOC
1)pOC含む骨髄細胞をupper well、recombinant CX3CL1をlower wellに用いchemotaxis assayを行った(A)。
2)pOCにおいて膜結合型のCX3CL1を用いて、adhision assayを行った(B)。
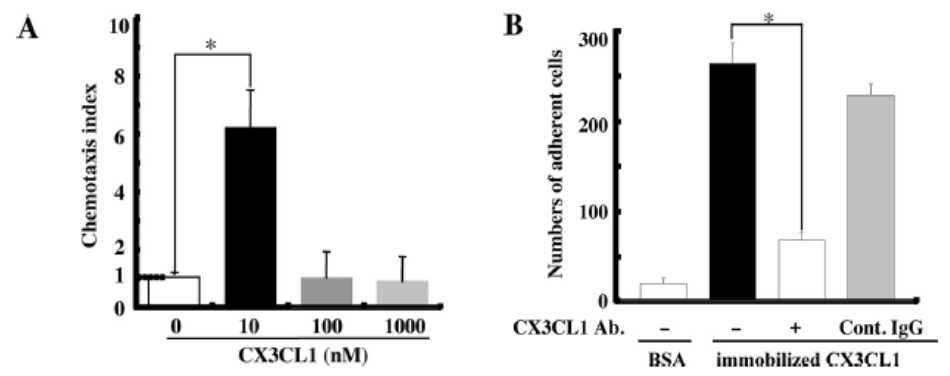 A, CX3CL1は細胞を遊走させる B, 膜結合型のCX3CL1は細胞を接着させる
A, CX3CL1は細胞を遊走させる B, 膜結合型のCX3CL1は細胞を接着させる
3)pOCをRANKL(100ng/ml)の存在下で培養(a)、CX3CL1(10nM)の存在下で培養しTRAP染色を行いosteoclastへの分化を確認しCX3CR1の発現をRT-PCRで確認
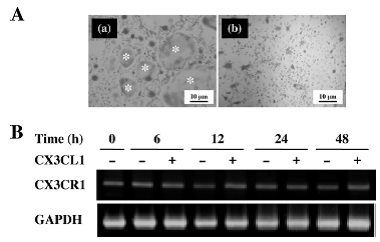
*CX3CL1は直接的にosteoclastの分化には関与せず、CX3CR1の発現も増加させない
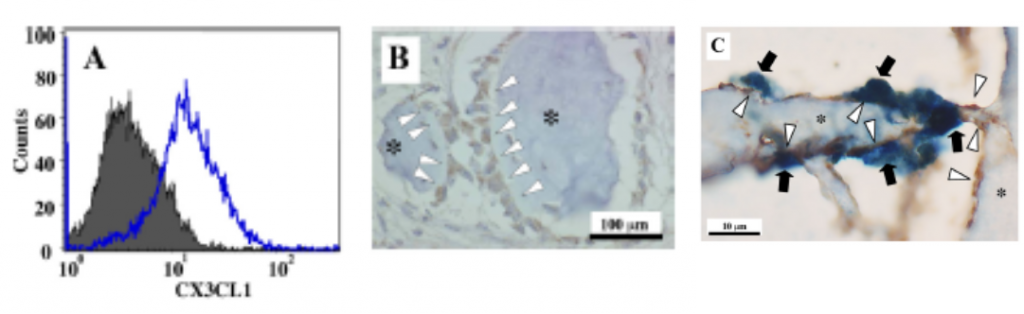 OsteoblastにはCX3CL1が高発現しており、免疫染色では骨の表面でCX3CL1陽性osteoblastとCX3CR1陽性pOCが並列し密に接着している。
OsteoblastにはCX3CL1が高発現しており、免疫染色では骨の表面でCX3CL1陽性osteoblastとCX3CR1陽性pOCが並列し密に接着している。
4.inhibition of osteoclast differentiation in vitro by anti-CX3CL1 mAb
1)mouseの骨髄細胞とosteoblastをvitamin D3の存在下で6日間培養し、TRAP染色
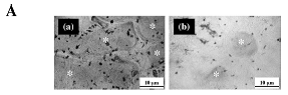 (a)control IgG (b)anti-CX3CL1 mAb
(a)control IgG (b)anti-CX3CL1 mAb
2)anti-CX3CL1 mAbを用いてmOCsの分化を確認し骨表面のTRAP陽性osteoclastを評価
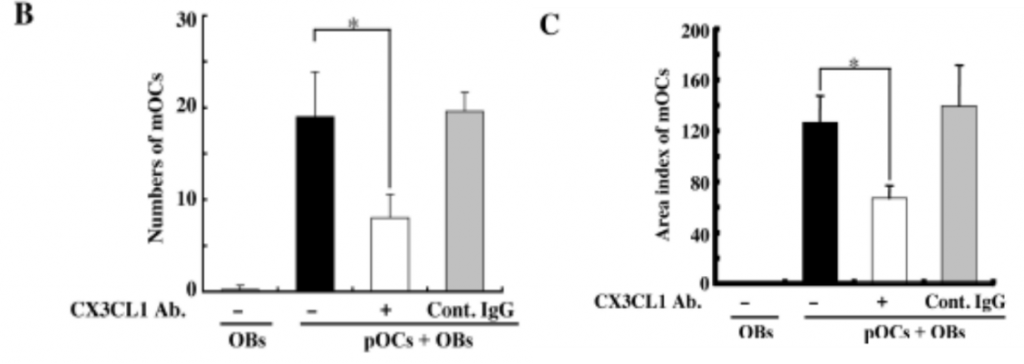 CX3CL1 AbはOCの成熟を抑制する
CX3CL1 AbはOCの成熟を抑制する
5.inhibition of bone resorption in vivo by anti-CX3CL1 mAb

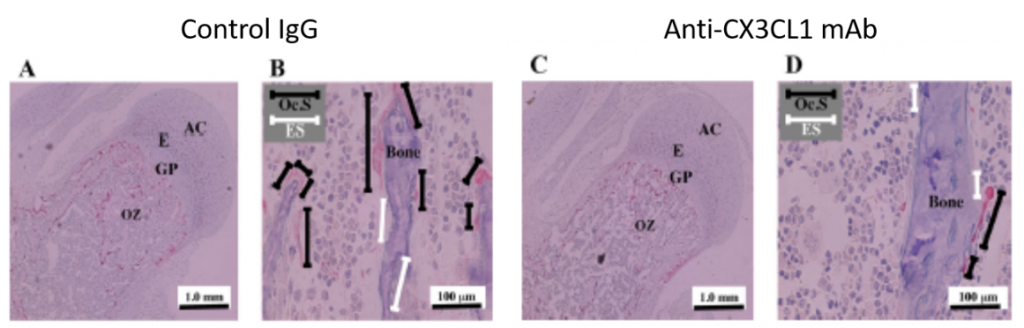
<conclusion>
Anti-CX3CL1 Abはosteoclastによる骨破壊を抑制する。それゆえに、CX3CL1-CX3CR1を抑制する事は、関節リウマチの関節炎、骨破壊の双方を抑制する事ができる可能性がある。
担当:古屋秀和






